|
|

|
Automated
analysis and design of LNG storage tank: reducing
engineers' time and time to market.
-
Paper
presented at
Gastech Exhibition and Conference, Milan, Italy, 5-8
September 2022 by Jesus Rodriguez of LUSAS.
-
This paper
describes an efficient design approach for LNG storage
tanks that adopts a 2D axisymmetric model for thermal
analysis, and a 3D shell model for structural loads,
considering seismic effects. This requires an
integrated methodology extending to the combination of
results and design checking, with detailed attention
to the varying reinforcement orientation.
-
Methods
have been developed based on the requirements of
ongoing LNG tank projects for companies such as KOGAS
(Korea Gas Corporation) and KGT (Korea Gas Technology
Corporation). These enable all the required design
checks to be performed in a single 3D shell model
bringing together results from thermal, seismic, and
staged construction analyses and allowing design
checks performed to various international
standards.
-
LUSAS
finite element analysis software was used to develop
the required tools to automate the modelling and
design of the storage tanks. Customisation and
automation through an open API enables users with
basic programming knowledge to create the various user
defined features required, extract results and combine
them with speed and accuracy in the desired format.
-
Solutions
to the challenges encountered have enabled
improvements in the efficiency of the analysis and
design process for LNG storage tanks to reduce the
engineers time and time to market by an estimated
20-30%.
-
View
paper
|
|
|
|
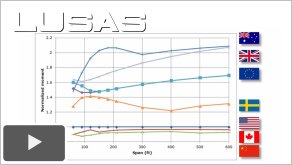
Traffic
loading code comparison of AASHTO, State implementations
and other international codes (13:14)
-
Paper
presented at
IABSE 2019, New York, USA, 4-6 Sepetember 2019 by
Terry Cakebread of LUSAS.
-
This paper
compares the traffic loading requirements and effects
according to AASHTO 8th LRFD (used directly by 26
States) and four sample states that include amendments
to that code, namely Kentucky, Maine, New York and
Pennsylvania, against those obtained from
international codes of practice including Eurocode EN
1992-1:2003, UK National Annexe (SV80 loading),
Swedish Complementary Load Model, Canada CSA S6-14,
Australia AS5100.2-2017 and China JTH D60-2015.
|
|
|
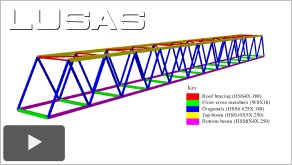
|
Steel
bridge member resistance: AASHTO compared to other
international codes (19:52)
-
Paper
presented at
NASCC 2019, St Louis, Missouri, USA, 3-5 April 2019 by
Terry Cakebread and Steve
Rhodes of LUSAS.
-
This paper
contrasts the different approaches to member
resistance calculations in AASHTO 8th edition,
Eurocode EN1993-2:2006 and Canadian Bridge Design
standard CSA S6-14. An example steel truss footbridge
is used to compare resistances and utilizations
determined from each Code (on the basis of identical
loading). AASHTO is found to be lacking two
interaction checks, to be unconservative in one check
and over-conservative in another by comparison to the
Eurocode – and prohibits the use of some members
based on slenderness alone. For its part, the Eurocode
is found to be more opaque in expressing one
interaction check and to be considerably more
voluminous in the calculations required to obtain
similar results.
-
View
paper
|
|
|
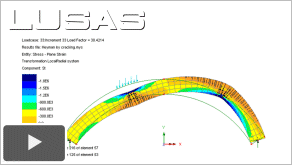
|
 Application
of Finite Element Methods to Masonry Bridges (10:18)
Application
of Finite Element Methods to Masonry Bridges (10:18)
-
Paper
presented at
the 40th IABSE Symposium (Nantes 2018), Nantes,
France, 19-21 September 2018 by Philip Icke and Steve
Rhodes of LUSAS.
-
Describes
and shows analysis techniques for 2D modelling of
cracking and crushing in arches, investigating ring separation, and modelling repairs using dowels in
arches to aid with general bridge management.
Soil-stucture interaction modelling is discussed prior
to showing how 3D solid models and layered shell
elements can be used in conjunction with a trilinear
soil model to investigate more detailed models that
may also include internal spandrel walls.
-
View
paper
|
|
|
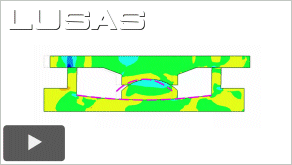
|
 Finite
Element Analysis of Joints, Bearings and Seismic Systems
(24:11)
Finite
Element Analysis of Joints, Bearings and Seismic Systems
(24:11)
-
Paper
presented at
the 8th World Congress on Joints, Bearings and Seismic
Systems, Atlanta,
Georgia, USA, 25-29 September 2016 by Terry
Cakebread of LUSAS.
-
Describes
and illustrates the different ways that joints,
bearings and seismic systems can be modelled, covering
the relevance of using different finite element joint
models in differing situations, These include
different ways to model lift-off behavior (smooth
contact or elastic-plastic joints); the use of more
advanced joints for modeling lead rubber bearings and
friction/pendulum bearings; why dampers and other
seismic systems are employed and the methods of
modeling them; and some more detailed bearing models
including carrying out bearing repairs in situ and
ways of modelling detailed bearing models with full
contact behaviour.
-
View
paper
|
|
|

|
 Integral
Bridges and the Modeling of Soil-Structure Interaction
(25:07)
Integral
Bridges and the Modeling of Soil-Structure Interaction
(25:07)
-
Paper
presented at the International Bridge Conference 2014 by Steve Rhodes and Terry
Cakebread of LUSAS.
-
At the time
of writing the paper, no standard approach for the analysis of
integral bridges appears in AASHTO LRFD Bridge Design
Specifications or other international codes. This
paper considers the approaches most suitable for
modeling common integral bridge forms, expanding upon
recent guidance regarding soil-structure interaction
approaches. Issues including material properties,
initial stress state and the incorporation of the
effects of soil ratcheting are discussed and both
continuum and spring-type finite element models are
explored.
-
View
paper
-
A similar
presentation for a paper presented at the European Bridge Conference
in 2015 referencing metric units can
also be viewed here.
|
|
|

|
 Understanding
Buckling Behavior and Using FE in Design of Steel Bridges
(28:13)
Understanding
Buckling Behavior and Using FE in Design of Steel Bridges
(28:13)
-
Paper
presented at the International Bridge Conference 2013 by Stephen Rhodes and Terry Cakebread of LUSAS.
-
Describes how Finite Element (FE) analysis can
be used to predict buckling modes, highlighting
methods which are practical for day-to-day use.
It explores some criterion which might be used
to identify if such behavior, including global
buckling modes, should be of concern to the designer,
drawing on recommendations including those in the
recently published NCHRP Report 725 and Eurocodes.
Use of FE in the determination of member
resistances is also explored.
-
View
paper
|
|
|
|
 Rating and
Upgrading of Steel Bridges using Finite Element Modeling
(27:39)
Rating and
Upgrading of Steel Bridges using Finite Element Modeling
(27:39)
-
Paper
presented at 7th New York City Bridge Conference
2013 by T. Cakebread and S. Rhodes of LUSAS.
-
Describes how Finite Element (FE) modeling
techniques can assist in the assessment (rating) and
upgrading of steel bridges of various types. Global
and local modeling options are considered with
reference to several projects, in particular the West
Gate Bridge in Melbourne, Australia. The use of
different analysis assumptions, element types,
eigenvalue and nonlinear analysis functions to achieve
greater load rating capacity is outlined, identifying
examples of good practice and drawing on international
codes and literature for recommendations.
-
View
paper
|
|
|

|
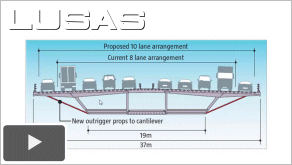
 Assessment and upgrading of Steel Bridges
using Finite Element Modelling
Assessment and upgrading of Steel Bridges
using Finite Element Modelling
-
As
presented at IABSE 2013 by Philip Icke and Steve
Rhodes of LUSAS.
-
This paper
describes how Finite Element (FE) modelling techniques
can assist in the assessment (rating) and upgrading of
steel bridges of various types. Global and local
modelling options are considered with reference to
several projects, in particular the West Gate Bridge
in Melbourne, Australia. The use of different analysis
assumptions, element types, eigenvalue and nonlinear
analysis functions to achieve greater load rating
capacity is outlined, identifying examples of good
practise and drawing on international codes and
literature for recommendations.
-
View
paper
|
|
|

|
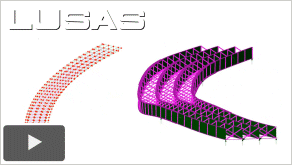
 The Benefits of
Elastic and Nonlinear FE Buckling Analysis Over a Codified
Approach (23:03) The Benefits of
Elastic and Nonlinear FE Buckling Analysis Over a Codified
Approach (23:03)
-
As
presented at a workshop session at NASCC (incorporating the World Steel
Bridge Symposium) 2012 by Terry Cakebread of LUSAS.
-
The
assessment or load rating of existing structures to
requirements is often over-conservative and can
suggest they can "fail" buckling checks, but
analysis with software can often reveal additional
capacity. For new structures, where buckling during
erection could be critical, FE analysis permits
additional checks to be carried out. For existing and
new structures, material and additional
bracing/stiffeners can be optimised by carrying out FE
analysis. See how this is done using LUSAS FE
software.
|
|
|
|
 3D
Considerations in Bridge Design (17:46)
3D
Considerations in Bridge Design (17:46)
-
As
presented to the AASHTO T-19 Technical Committee in
2012 by Terry Cakebread of LUSAS.
-
This
presentation considers the different modelling
approaches used for different bridge types; the types
of analyses involved; why a 3D model may be required;
and what is involved in building and solving such a
model
|
|
|

|
 The
Benefits and use of FE modelling in Bridge Assessment
and Design
The
Benefits and use of FE modelling in Bridge Assessment
and Design
-
As
presented at IABMAS 2012 by Philip Icke of LUSAS and
Carlo Margheritti of LUSAS (Italia).
-
Structural
analysis has progressed a long way from hand
calculations and from when distribution factors first
started to be used. From the first computer methods,
grid and grillage analysis techniques evolved, leading
through progressive enhancements to the advanced 3D
graphical and analytical tools that we see and use
today. Finite element (FE) modelling and analysis is
being used more for bridge engineering because of the
more economical and accurate assessments and designs
its use produces. This paper illustrates the role that
it can play in just some areas of bridge analysis,
assessment and design with reference to bridge
assessments and designs carried out by consultants on
projects around the world.
-
View
paper
|
|
|

|
 What a difference a day makes
- how analytical effort saves structures (27:45)
What a difference a day makes
- how analytical effort saves structures (27:45)
-
As
presented at the International Bridge Analysis Seminar
2012 by Chris Hendy, Head of Bridge
Design and Technology, Atkins.
-
The benefits obtained from
using linear and nonlinear analysis to assess a number
of bridge structures of both steel and concrete
construction is described. The reasons behind the need
for a detailed structural assessment of the regions of
interest for each bridge are also briefly explained
and the assessment and analysis methods used are
covered in more detail showing that potential savings
by reducing / eliminating strengthening can more than
compensate for the additional asessment cost.
-
This is a
restricted presentation. Please contact support@lusas.com
if you wish to view this.
|
|
|

|
 Structural
Idealisation for Assessment (20:21)
Structural
Idealisation for Assessment (20:21)
|
|
|

|
 Steel
Bridge Assessment (19:07)
Steel
Bridge Assessment (19:07)
|
|
|

|
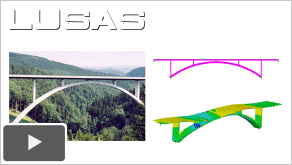
 West Gate Bridge
Upgrade (17:03)
West Gate Bridge
Upgrade (17:03)
-
As
presented at the International Bridge Analysis Seminar
2012 by Peter Robinson of Flint
& Neill.
-
The West Gate Bridge
upgrade works were undertaken by an Alliance in which
Flint & Neill had the major responsibility for the
assessment and strengthening design for the steel
bridge; advice on inspection, operation and
maintenance; developing designs for early works
improved access; and for producing a current set of
electronic as-built drawings from historical documents
and original drawings. In this presentation the use of
global and local finite element analysis for
strengthening of the steel box girder, by cantilever
propping, internal stiffening, and post-tensioning;
and for the management of construction loads is
described.
-
This is a
restricted presentation. Please contact support@lusas.com
if you wish to view this.
|
|
|
|
 Modelling
Concrete Bridges for Assessment (21:44)
Modelling
Concrete Bridges for Assessment (21:44)
|
|
|
|
 LUSAS Concrete
Material Models - Theory (27:20)
LUSAS Concrete
Material Models - Theory (27:20)
-
As
presented at the International Bridge Analysis Seminar
2012 by Tony Jefferson of Cardiff
University.
-
The
presentation provides insight into the material models
which control the behaviour of concrete in LUSAS. The
presentation concentrates on the simulation of
cracking and crushing behaviour but also describes a
recently developed model for early age concrete
behaviour. A
particular focus is on the
importance of modelling crack closure behaviour and
aggregate interlock. The inaccuracy
in predictions which do not account for such behaviour
(as is the case with many existing concrete models) is
highlighted using results from an experimental
reinforced concrete beam.
-
This is a
restricted presentation. Please contact support@lusas.com
if you wish to view this.
|
|
|
 Masonry
Arch Assessment (14:41)
Masonry
Arch Assessment (14:41)
|
|

|
 Assessment of Brick
Vaulted Arches (23:22)
Assessment of Brick
Vaulted Arches (23:22)
-
As
presented at the International Bridge Analysis Seminar
2012 by Danny Boothman of URS.
-
This
presentation provides
an overview of the Platforms 12 & 13 Design &
Build Contract at Glasgow Central Station, which
required the provision of support to 2x340m of new
permanent way (P-way), and goes on to explain how
detailed assessment of vaulted arch geometries
(that were constructed in the early 1900’s and not
previously exposed to rail loading) were analysed
using LUSAS to confirm their adequacy for the required
RA8 assessment loading.
-
This is a
restricted presentation. Please contact support@lusas.com
if you wish to view this.
|
|
 |
 The Use of Finite Element Analysis in the
Design of Footbridges
The Use of Finite Element Analysis in the
Design of Footbridges
-
As
presented at Footbridge 2011 by Philip Icke of LUSAS.
-
This paper
aims to highlight the benefits of using finite element
(FE) analysis for different types of footbridge design
and illustrate those benefits with reference to a
diverse range of urban regeneration footbridges of
various construction materials. Key analysis tools
highlighted include those for calculating member
resistances for linear and nonlinear buckling
analysis, dynamic analysis capabilities, pedestrian
loading, energy dissipation devices and staged
construction modelling. The paper concludes that the
use of finite element analysis can lead to more
efficient, cost-effective footbridge designs and that
its use is just as valid for low-cost
"practical" footbridges as it is for the
design of more technically advanced and expensive
"iconic" structures.
-
View
paper
|
|
 |
 Finite Element Analysis of Joints, Bearing
and Seismic Systems
Finite Element Analysis of Joints, Bearing
and Seismic Systems
-
As
presented at IJBRC 2011 by Terry Cakebread of LUSAS.
-
Describes
and illustrates how advanced Finite Element Analysis
(FEA) software has been used to model joints, bearings
and seismic systems on a variety of projects
worldwide. The paper illustrates the different ways
that bearings can be modeled and covers the relevance
of using different finite element joint models in
differing situations, including different ways to
model lift off behavior (smooth contact or
elastic-plastic joints); highilights the use of more
advanced joints for modeling lead rubber bearings or
friction/pendulum bearings; discusses why dampers and
other seismic systems are employed and covers the
methods of modeling them. Examples of detailed bearing
models with full contact behavior are shown.
-
View
paper
|
|