Software Tour
Load types and
combinations
LUSAS Bridge provides a
comprehensive range of general loading types to cater for most
circumstances. Vehicle load types, train loading, and prestress and
post tensioning to many international design codes are also provided.
Vehicle load optimisation facilities help find onerous traffic
patterns. Envelopes, basic and smart load combination facilities help
investigate maximum and minimum primary and coincident effects.
General loads
Structural,
prescribed and thermal loads are feature based loads that are
assigned to the model geometry and are effective over the whole of
the feature to which they are assigned.
- Apply structural loadings
that include gravity, concentrated, distributed, face, temperature,
stress/strain, and beam loads.
- Specify initial
displacements, velocity or acceleration using prescribed loading
options.
- Use discrete loads
to distribute a loading pattern over full or partial areas of the
model independent of the model geometry.
- Define compound
loads (to define load trains) from a set of previously defined
discrete loads and assign to a model as one loading.
- Use thermal loads to
describe temperature or heat input for a thermal analysis or coupled structural / thermal analysis.
- Apply variations in
loading to all feature load types according to the feature on
which they have been assigned.
Prestress and
post-tensioning loading
Prestress /
post-tensioning in LUSAS is
suitable for beams, slabs and volumes, and for certain design
codes can incorporate time-stage
with creep and shrinkage. LUSAS calculates equivalent nodal loading due
to any tendon prestressing or post-tensioning and assigns these forces
automatically to beam, shell, or solid elements of a model
for a chosen loadcase or set of loadcases. Span-by-span, progressive
placement, balanced cantilever and incremental launching time staged construction methods are
supported.
Design codes
supported include:
- AASHTO
LRFD 2nd Edition
- AASHTO
LRFD 5th to 7th Edition
- BS5400-4:1990
- DD
EN1992-1-1:1992 Eurocode 2
- EN
1992-1-1:2004 Eurocode 2
- JTG
D62-2004
|
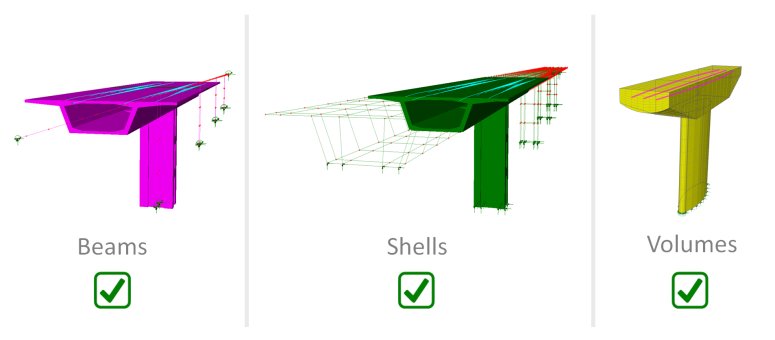
|
|
Beam (line),
shell (surface) and solid (volume) modelling of concrete is
supported. |
In summary:
- Define tendon profiles and
view the developing tendon shape in real-time as it is being defined,
or copy and paste data from a spreadsheet. Tendons can also be
generated by selecting lines, arcs or splines that are defined
or imported into LUSAS Modeller.
- Manual definition by
coordinates in 3D space or by defining coordinates in two
2D planes is supported.
- Locally defined tendon profiles can be used
anywhere in the model and any number of times.
- Define tendon
properties and values/settings relating to instantaneous and
time-dependent losses.
- Elastic
shortening due to stressing of other tendons according to the selected
design code or user-defined percentage losses is taken into effect.
Time dependent effects can also be considered.
- Simply assign the
tendon loading by dragging and dropping it onto selected line, surface or volume features in a
model for a single or a range of loadcases.
- Produce graphs of
tendon prestress force after time-dependent losses.
-
Add tendon properties, profile, loading, losses and setting-out data
for all tendons assigned to a model to a model report.
|
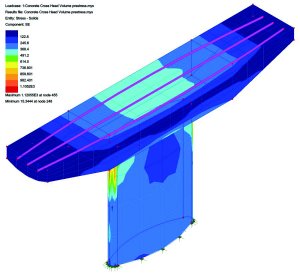
|
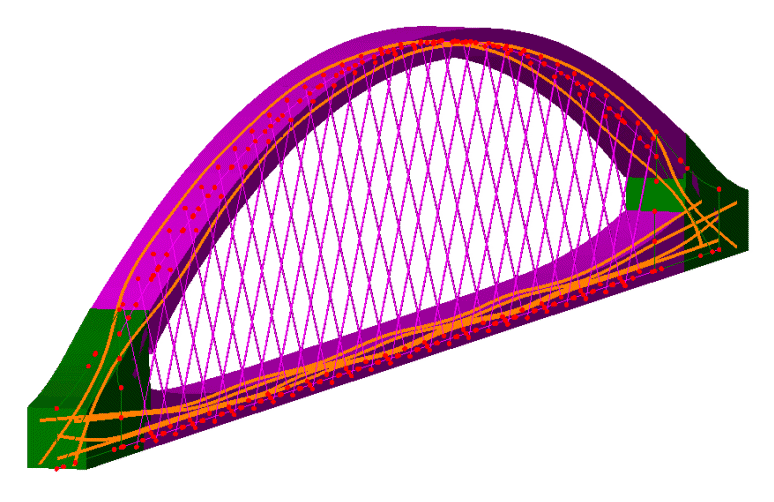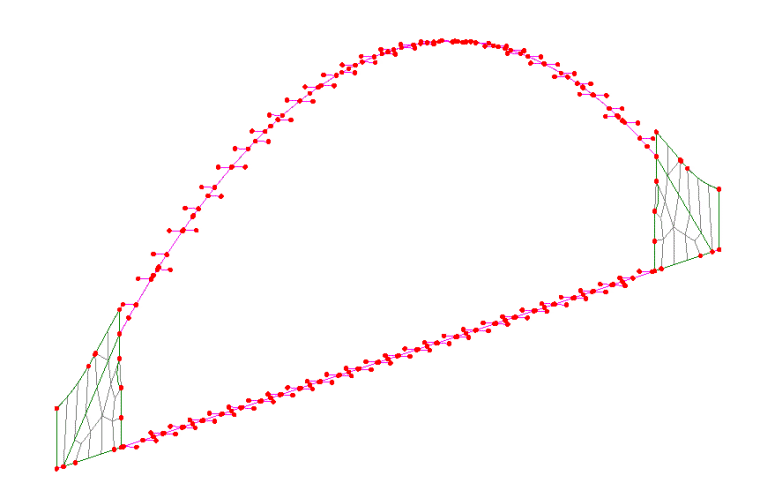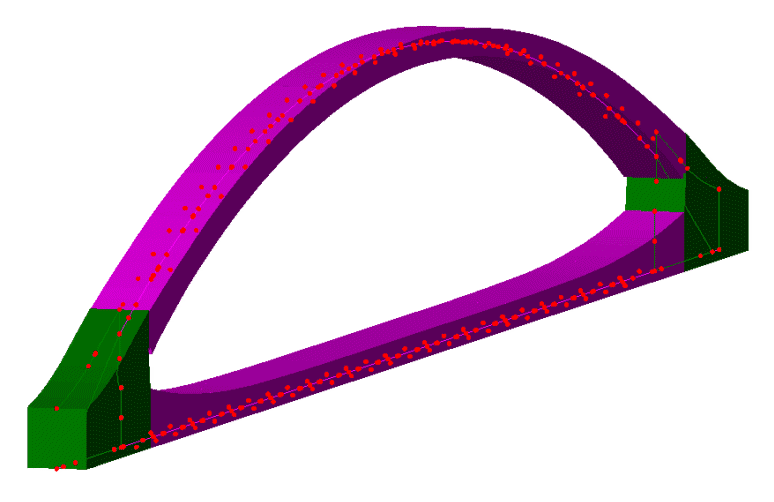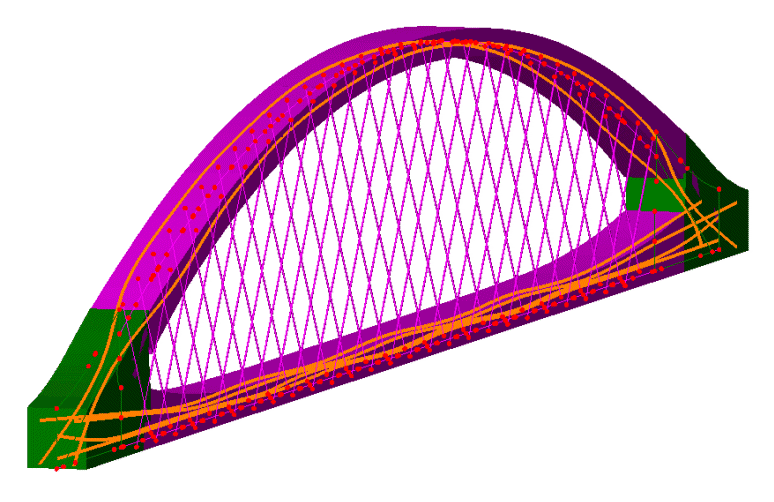
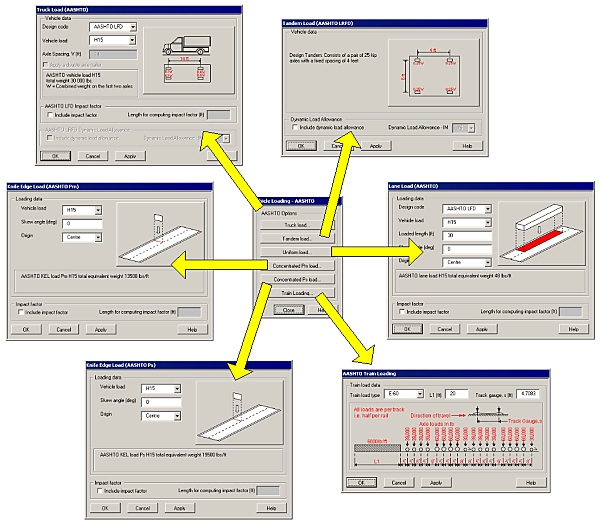
Vehicle loading
Vehicle
loading facilities in LUSAS Bridge software make the generation of
live loads very straightforward, significantly speeding up the task of defining the
loading on a bridge deck. They comprise:
Static vehicle loading
Static vehicle, lane, and knife edge loading
types are provided for many international bridge design codes. These
currently include:
-
AUSTROADS Bridge Design Code
HB77.2, AS 5100.2-2004, AS 5100.7-2004. (Australia)
-
Canadian Highway Bridge
Design Code (CHBDC.)
-
JTG D60-2004 General
Code for Design of Highway Bridges and Culverts. Peoples Republic
of China)
-
Special vehicles defined as
Load Model 3 (LM3) in the Danish National Annex to EN1991-2
(Denmark)
-
EN1991-2:2003 Eurocode 1:
(Eurocode) including any country-specific load models as part of a
country's National Annex to the code.
-
TIEL 2172072-99 and the
National Annex EN1991-2 (Finland)
-
IRC:6-2000 Section: II Loads
and Stresses. (India)
-
Israeli loading design code.
-
Korean loading code
-
NATO vehicle loading defined
in annex A of STANAG 2021
-
New Zealand loading code
-
Norwegian loading design code
-
Poland loading code
-
TMH7 Code of Practice for the
Design of Bridges and Culverts
-
BRO Classification loads
(Sweden
-
BS5400, BD37/88, BD37/01,
BD21/97, BD21/01, BD 86/11 and EN1991-2 National Annex 2.16
(United Kingdom)
-
AASHTO
LFD and LFRD loading, and selected state dependent design loading
-
Additional loading types are being added all the time.
Train loading
Train loading options for many international bridge design codes
including AASHTO and Eurocode are provided.
|
Load trains
- Load trains can be
created using a compound load facility.
Abnormal loading
- Abnormal load generators
are included.
Moving load generators
- Static vehicle and train
loadings can be used either on their own or with a moving load
generator to automatically create the required set of loadcases as
a loading type makes its way across a bridge.
|

|
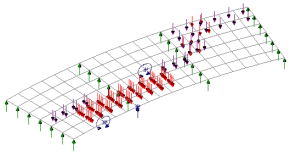
Vehicle Load
Optimisation
Significant amounts of
time can be saved with the Vehicle Load Optimisation software option,
which automatically generates the most adverse live load patterns for
multiple lanes of vehicle (road) traffic, or tracks carrying train
(rail) loading, in accordance with a variety of international design
codes. The input of a few parameters enables an optimised load pattern
to be generated for shell/plate element models and line beam models
(vehicle loading only).
 |
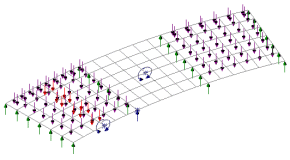 |
| Vehicle
load optimisation |
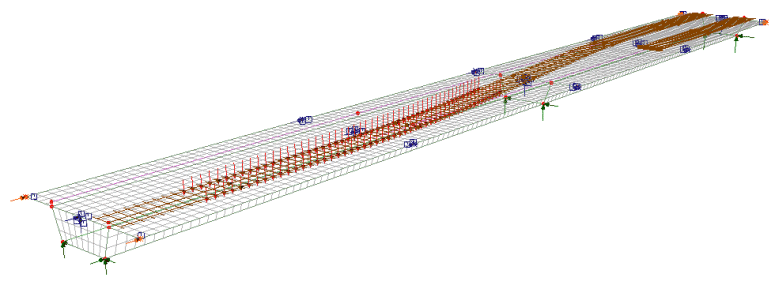
|
| Rail
load optimisation |
Vehicle load
optimisation reduces the amount of time spent generating loadcases to
replicate live loading on models, and leads to more efficient and
economic design, assessment or load rating of bridge structures.
For more details see Software Option - Vehicle Load Optimisation
Response
spectra
Design code
response spectrum data for the following codes of practice are
currently supported:
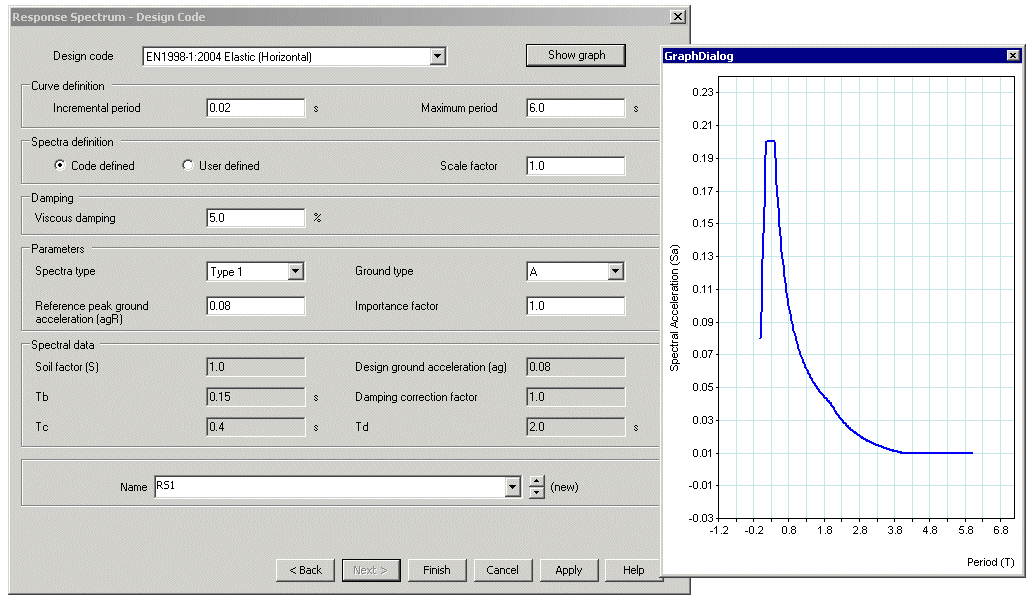
Envelopes and combinations
A key feature of LUSAS
Bridge is the
Basic, Smart and Code-specific load combination facilities which allow manual or fully
automated assembly of design load combinations. From these, envelopes, contour and
deflected shape plots, and results graphs can be readily obtained for any loadcase under
consideration.
-
Basic load combinations allow for manual definition of loadcases and
load factors.
-
Envelopes of multiple
loadcases create maximum and minimum results.
-
The Smart Combinations facility
automatically generates maximum and minimum load combinations from the applied loadings to
take account of adverse and relieving effects. This enables the number of combinations and
envelopes required to model a bridge to be substantially reduced. Absolute maximum
envelopes are included.
Design code load
combinations
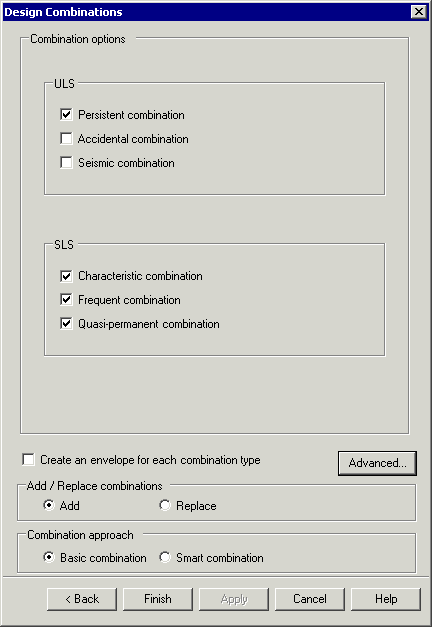
Use the
Design Combination wizard to assign a loadtype to a loadcase, envelope or basic combination
for a supported design code. Based on the assignments and settings
made, design code load combinations for those load types are automatically
generated by LUSAS Modeller.
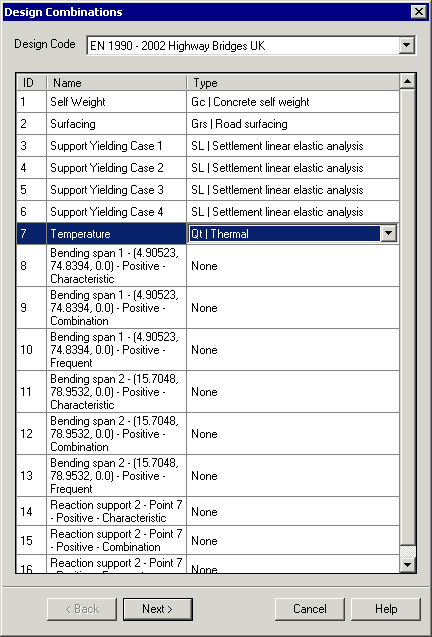 |
|
|
| Loadcase
/ loadtype definition |
Combination
options
|
|
|
|
Design
combinations for the following codes of practice are supported:
- AASHTO
7th Edition
- AS/NZS
1170
- BD21/01
- BD37/01
- CSA-S6-14
- EN1990
(Buildings) Recommended Values
- EN1990
(Buildings) to Irish National Annex
- EN1990
(Buildings) to UK National Annex
- EN1990
(Bridges) Recommended Values
- EN1990
(Bridges) to Irish National Annex
- EN1990
(Bridges) to UK National Annex
- GB
50009 - 2012
- JTG
D60-2004
|
|
Staged
construction modelling
Find out more
|